Cloud computing is a computer system that operates by the joint action of disparate elements brought together regardless of their geographical location and underlying infrastructure. Simply put, it is the delivery of computing services (servers, storage, databases, networking, software, analytics) over the Internet to provide more flexible resources to people and businesses.
The cloud allows you to rent your IT instead of buying it. Instead of investing heavily in databases, software and hardware, companies choose to access this computing power via the Internet and pay for it based on usage. When a company "goes to the cloud," it means that its IT infrastructure is stored offsite in a datacenter managed by the cloud provider. Instead of spending money and resources on legacy IT systems, customers can focus on more strategic tasks. Without making a significant upfront investment, companies can quickly access the IT resources they need and pay only for what they need.
The cost, scaling, performance and reliability advantages of cloud computing over a traditional approach are driving companies around the world, large and small, to migrate to cloud solutions.
A distinction is typically made between a public cloud owned and operated by a third-party cloud service provider that offers compute resources such as servers and storage, and a private cloud used exclusively by a company or organization. The hybrid cloud is a symbiosis of the two powered by technology that allows for data and application sharing.
Solutions as a service
Most cloud services can be classified into four broad categories: IaaS (infrastructure as a service), PaaS (platform as a service), SaaS (software as a service) and serverless computing. IaaS allows you to rent an IT infrastructure from a cloud service provider with a payment based on usage. PaaS are services that provide an on-demand environment for developing, testing, delivering and managing software applications (developers can quickly create web or mobile applications without the need for a server).Developers can quickly create web or mobile applications without having to worry about configuring or managing the server, storage, network and database infrastructure required for development.) With SaaS, cloud service providers host and manage the software applications and underlying infrastructure, and manage maintenance, such as software upgrades and security patches. Users connect to the application via the Internet, typically through a web browser on their phone, tablet or PC. Finally, serverless computing overlaps with PaaS by focusing on building application functionality without the time-consuming and ongoing management of servers and the infrastructure required to do so.
As you can see, cloud computing offers multiple functionalities to individuals but especially to companies, whether it is to create native cloud applications, store, back up and recover data, distribute content, and so on.It can be used to create native cloud applications, store, backup and retrieve data, deliver content or software on demand, test and generate applications, analyze data or incorporate intelligent models to interact with customers.
This market is expected to grow strongly over the next ten years. Ark Invest predicts that this market will be worth nearly $10 trillion by 2030.
Here is a projection of the combined market capitalization of all public cloud services combined (IaaS, SaaS, PaaS, serverless computing) for 2022 :
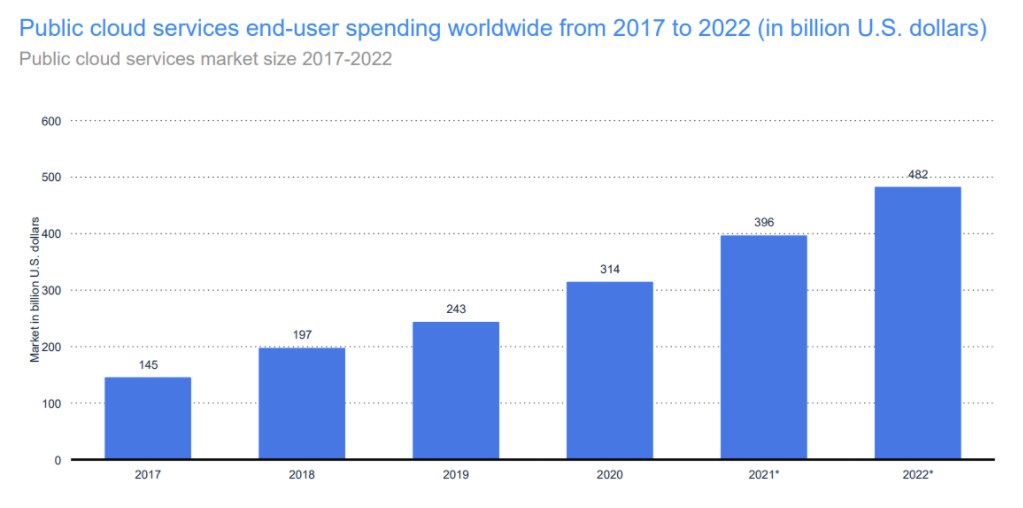
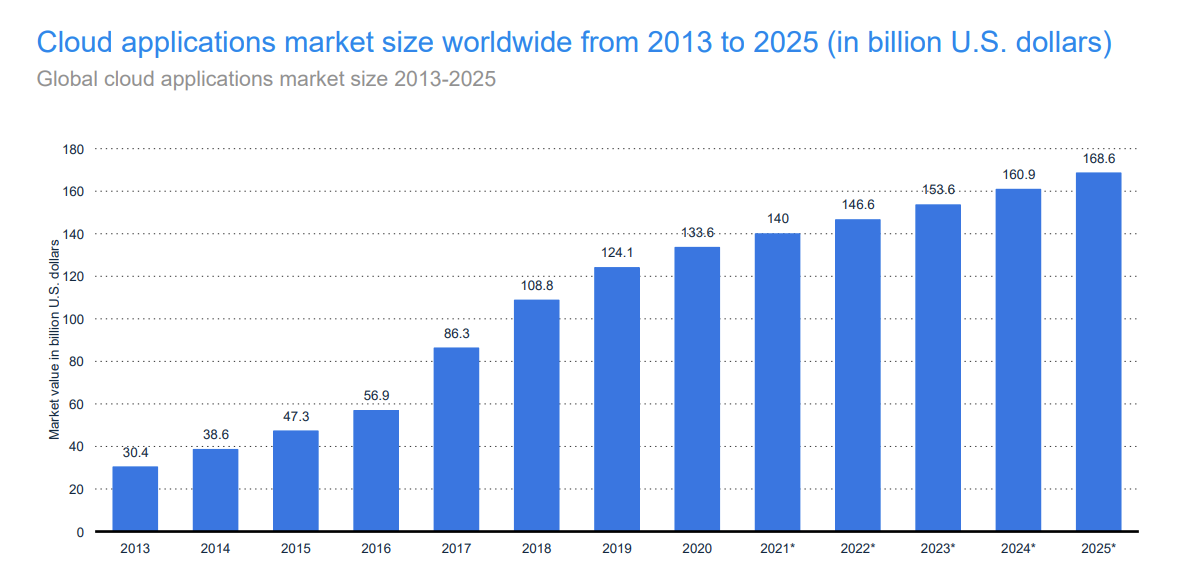
A projection of the cumulative market capitalization of cloud applications by 2025:
The cloud war has already begun:
In this little game, the web giants, including Alphabet, Meta, Microsoft and Apple have already positioned themselves as specialists. Their Chinese counterparts (Alibaba, Tencent, JD.com) have also entered the race. We also find Salesforce, IBM and Oracle well placed in the ranking. They all want to be the first and are investing massively in their infrastructures. Indeed, the effect of scale is important in order to reduce costs and offer a solution that becomes the standard for companies (a bit like Microsoft has managed to do with its Office suite). The most successful solutions are likely to win the largest market share in each industry, as customer retention is the driver of profitability in a scalable business like the cloud. Amazon Web Services (AWS) is the competitor to beat so far with 32% market share and still holds a lead over its rivals. The top 8 cloud providers control 80% of the market share.
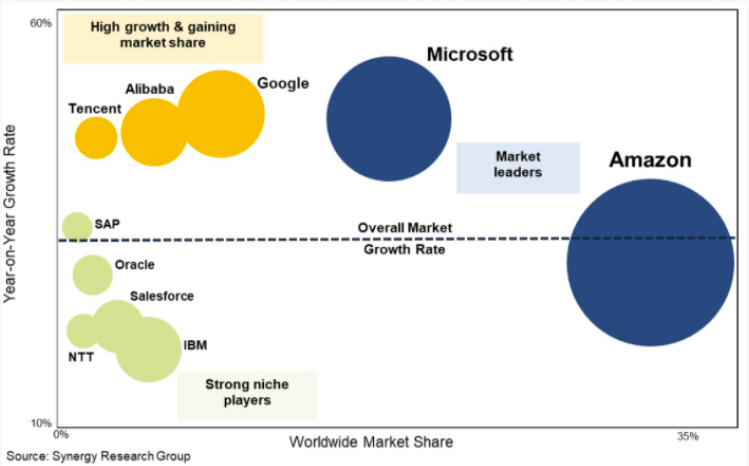
Source: Synergy Research Group
We can also mention smaller (and riskier) players, each with their own specificities but with great long-term potential, such as ServiceNow and Intuit.
If you wish to consult the thematic list of cloud computing players, MarketScreener experts have identified for you the main cloud computing players on a global scale. This list is limited to 100 companies selected according to fundamental criteria and capitalization filters.

 By
By 
















