Following an accident, vehicle owners are faced with a choice: either undertake the repair of their damaged vehicle or place it in the care of their insurance provider. Opting for the latter, the insurance company is left with the task of selling the compromised vehicle. This is precisely where Copart assumes a pivotal role, as insurers can entrust their vehicles to the company, which boasts an extensive network to facilitate the sale process through their specialized platform. In return for these services, Copart levies a fee, and upon the successful sale of the vehicle, retains an additional percentage, either fixed or variable, of the total transaction value.
This business model creates value for its clientele. Copart distinguishes itself within the market by delivering top-tier services. The auction platform itself presents comprehensive vehicle imagery, and estimates of post-repair value, along with projected repair costs, fostering seamless communication between buyers and sellers.
The company facilitates the sale of vehicles to buyers spanning across more than 190 countries via its online platform. Additionally, it operates over 200 storage facilities in 11 countries worldwide, including the United States, Canada, Brazil, Spain, Germany, the United Kingdom, Ireland, Oman, Bahrain, and the United Arab Emirates. Copart further provides a shipping service, enabling buyers to procure vehicles from virtually any location. This extensive infrastructure creates an expansive network of potential customers, endowing Copart's clients with an advantage in the industry.

Copart stands as a vanguard in its industry, underpinned by an expansive customer network that generates a cascading impact. Its good reputation and the organic proliferation of endorsements continually attract fresh clientele, akin to the trajectories charted by industry giants like Microsoft and Apple. Integration into the Copart ecosystem helps businesses aspiring to augment profitability, broaden their market footprint, and cultivate partnerships with emerging insurance entities. Recently, the company has expanded into the German market, increasing its large sales network, territorial array of storage infrastructure, and benchmark online platform constituting a wide MOAT.
Copart's revenue stream also resides in its secondary income source: direct vehicle sales. This offering, accessible through its website and specialized subsidiaries such as Cash for Cars, Powersport Buyers, Motorcycle Buyers, and National Powerhouse Auctions, empowers the company to target complementary markets encompassing motorcycles, watercraft, caravans, and snow sports. Although regarded as a supplementary revenue stream, this sector harbors substantial growth potential, particularly in regions worldwide where demand for these products surges, affording Copart the opportunity to bolster its profits by expanding its presence in these auspicious markets.

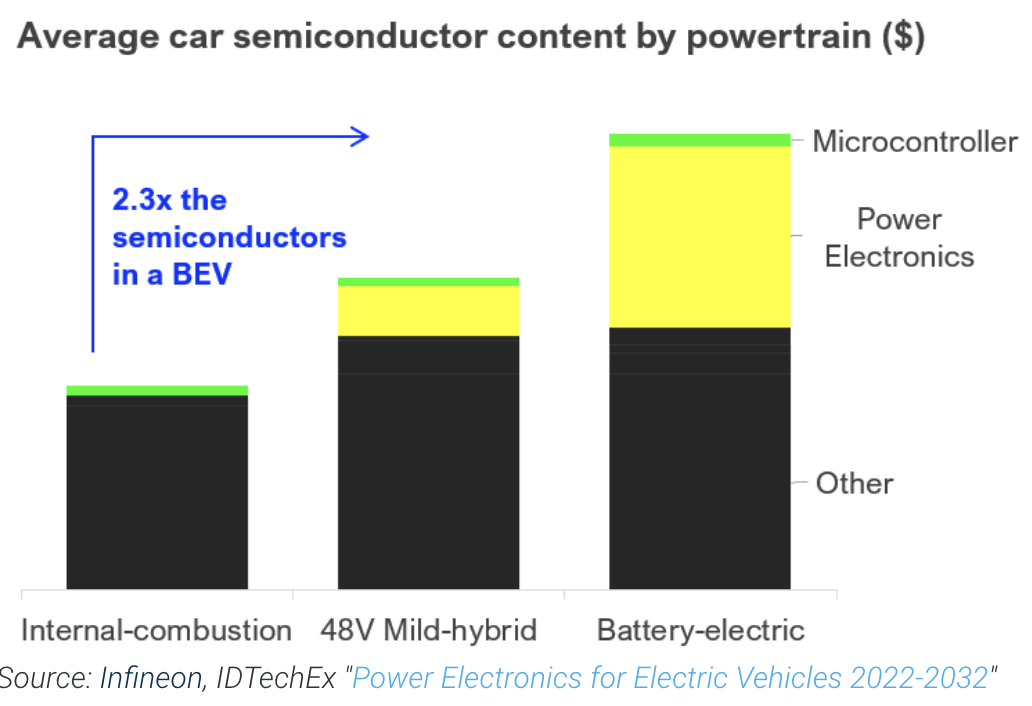
The automotive landscape is witnessing a notable evolution marked by increased technological sophistication and heightened safety standards. Contrary to conventional expectations, Copart finds itself in a favorable position amidst these developments, reaping substantial benefits. The company particularly capitalizes on elevated repair costs and the growing complexity of repair processes. Contemporary automobiles are equipped with an impressive array of technology, featuring anywhere from 3,000 to 5,000 integrated microchips—a stark contrast to the mere 300 chips found in vehicles just a few years ago.
This upward trajectory is poised to persist, notably with the proliferation of electric vehicles, which incorporate 2.3 times as many microchips as their internal combustion engine counterparts. Consequently, automobiles are evolving into increasingly intricate and technologically advanced machines, rendering repairs more intricate and demanding. This heightened complexity, in turn, augments the rate at which vehicles are declared unrecoverable, prompting owners to consider vehicle disposal. As a direct consequence, Copart experiences a surge in the volume of vehicles entering its purview.
Copart's strategic positioning endows it with a degree of resistance to economic cycles. During periods of heightened demand, characterized by a surge in new vehicle purchases, it acquires a substantial inventory of older models. During economic downturns when new vehicle sales wane, the company strategically accelerates the divestment of its inventory to sustain an aging fleet. This approach ensures the company's resilience across the various phases of economic cycles. Modern cars prioritize safety by using materials that absorb impact energy, but this leads to more frequent and expensive repairs, benefiting Copart's recovery rate.
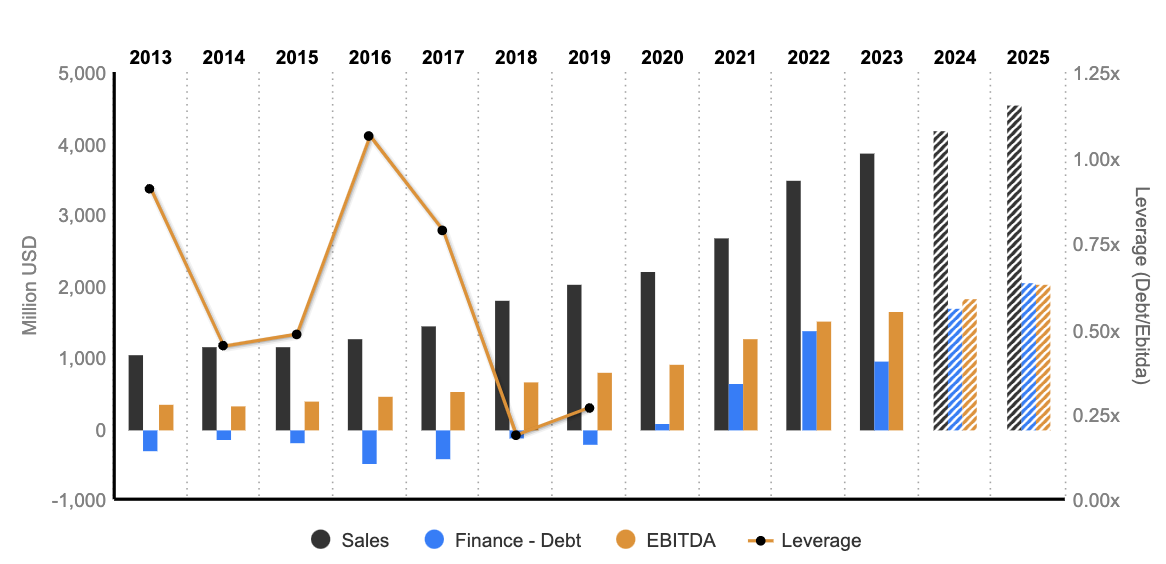
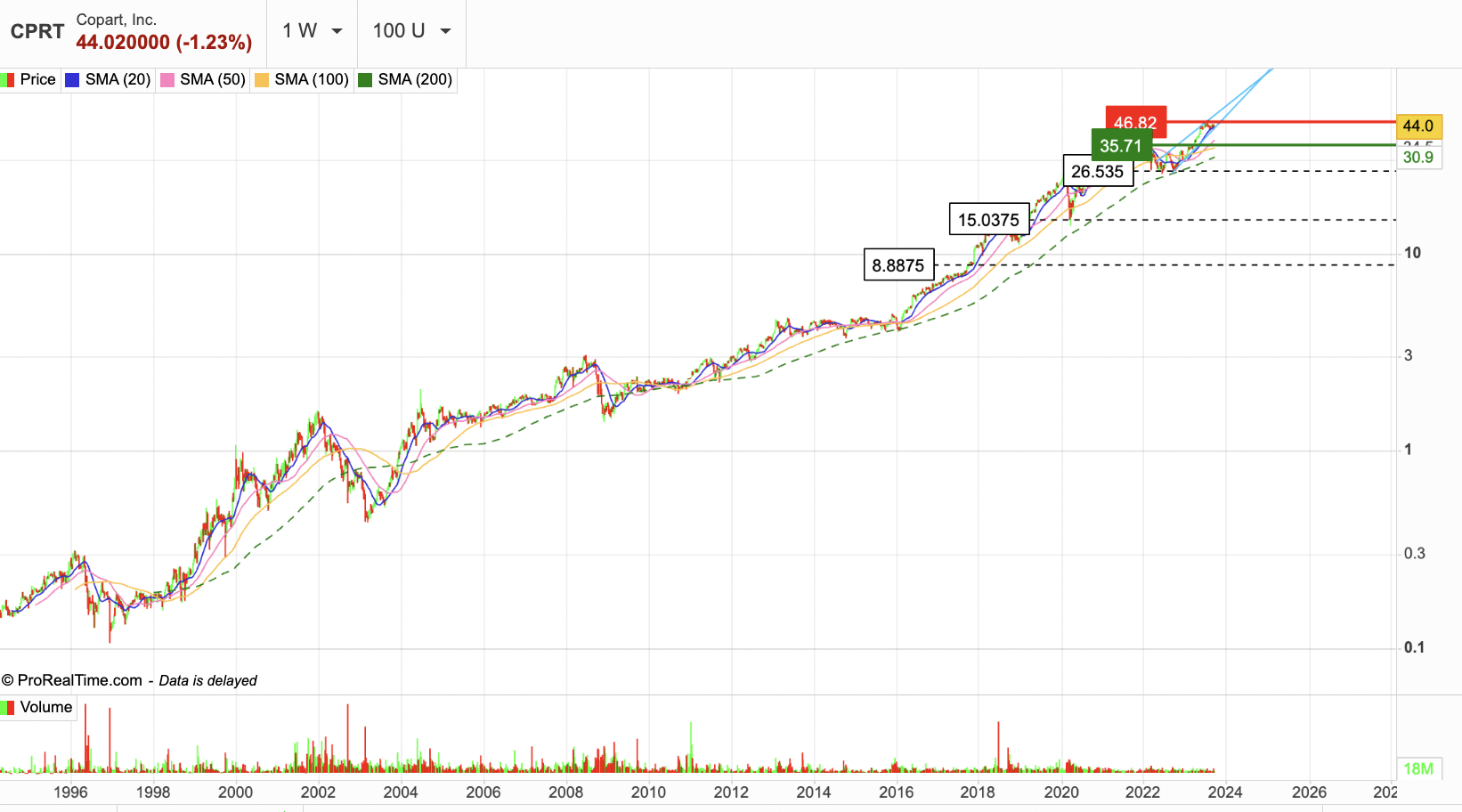
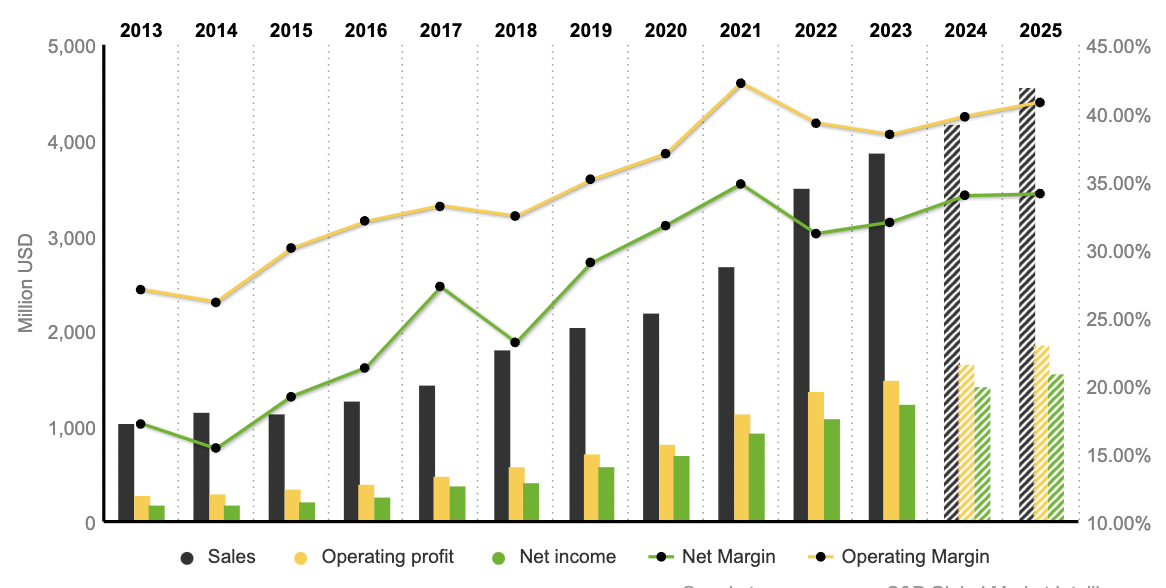
Over the past decade, the Group has demonstrated significant positive growth in its financial results. Sales have surged from $1,046 million to $3,870 million, marking a remarkable increase of 270%. EBITDA and EBIT have mirrored this upward trajectory, advancing from $340 million to $1,646 million and $283 million to $1,487 million, respectively. The operating margin consistently maintains a robust level of approximately 40%, while the net margin stands in close proximity at nearly 35%.
In the year 2023, the company anticipates reaching a Free Cash Flow (FCF) of $848 million, coupled with FCF margins approaching 25%. Notably, Net Income Before Interest (NBI) has experienced an exceptional ascent, surging by an impressive 652% over the same duration.
Nevertheless, it is worth noting that the enterprise presently commands a slightly elevated P/E ratio compared to its historical average. The current PER stands at 34.5x earnings, contrasting with the historical figure of 28.0x.
Return on Equity (ROE) has exhibited a declining trend in recent years, recording a value of 22.9% in 2023, with a forecasted figure of 19.1% for 2024, compared to the 2013 level of 27.2%. Concurrently, Return on Assets (ROA) maintains stability around the 20% range but is anticipated to gradually decrease to 17% and 14.7% by 2024-2025.
Despite the company's sustained growth spanning over five years, accompanied by robust financial health and impressive profitability, there remain certain risks that warrant careful consideration.
The advent of autonomous vehicles appears to promise the elimination of accidents, which fundamentally challenges the foundation of Copart's business model. However, the company presents data indicating that accidents have not decreased since the introduction of autonomous driving. This paradoxical phenomenon can be attributed to the complex task of programming machines to anticipate human behavior, and vice versa. The repair costs associated with autonomous vehicles surpass those of conventional cars, which ultimately augments Copart's business prospects. It is worth noting that many individuals deactivate driver-assist features, such as the automatic lane-keeping assistant, when they relinquish the act of driving. The realization of a society predominantly composed of autonomous vehicles remains a vision for the future, contingent upon factors such as affordability and appeal to the middle-class populace.
Copart has established a robust business model that gives it a solid advantage, setting the stage for long-term growth. This growth is expected to be further fueled by ongoing developments in the automotive market.

 By
By 


